Patient Information Leaflet
Heparin sodium (Beprin) solution for injection 5000ml
Heparin sodium (Beprin) solution for injection 1000ml
1. What beprin injection is and what it is used for
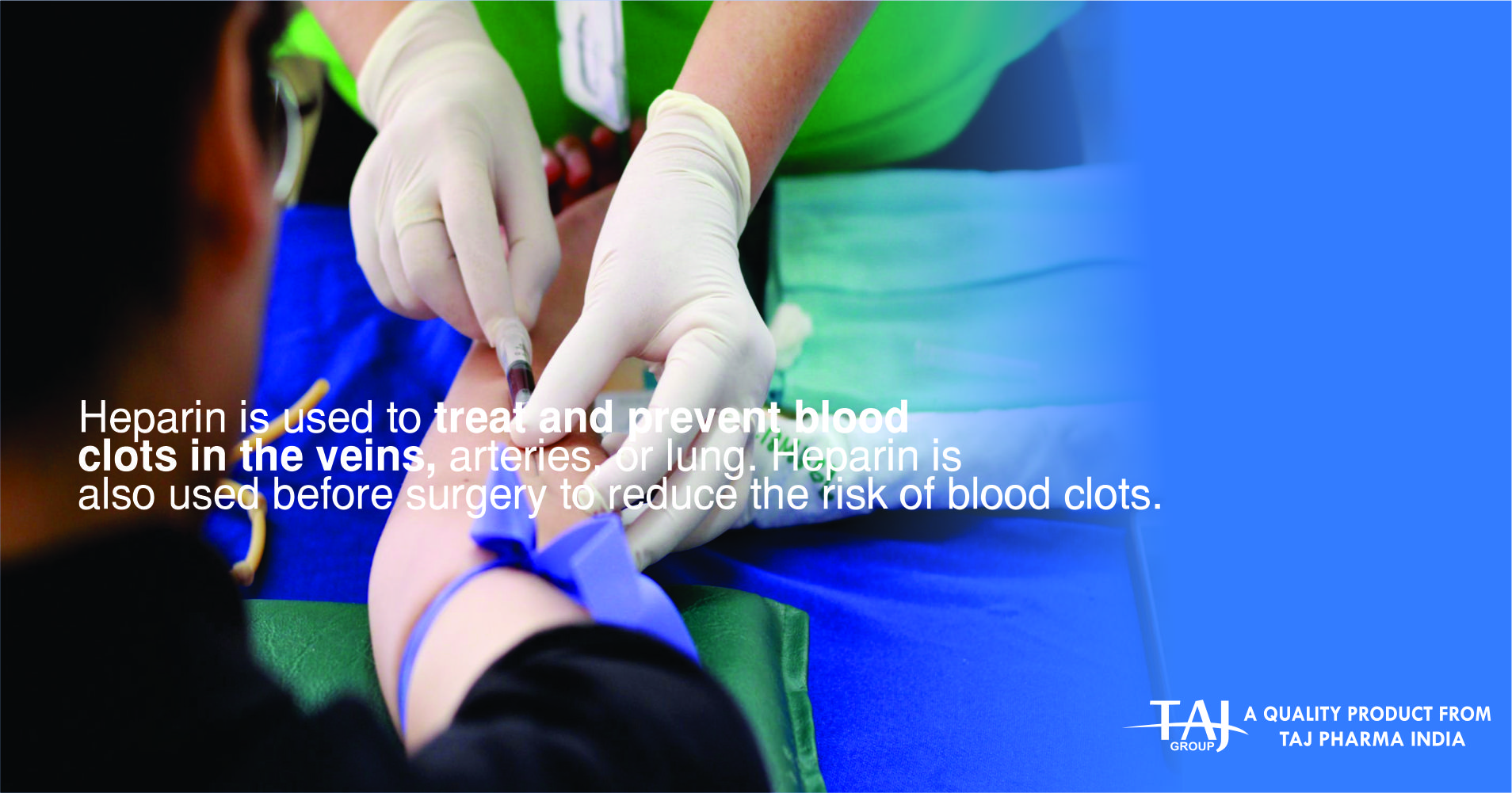
Heparin belongs to a group of drugs that are called anti-coagulants. These help to stop blood clotting. Beprin injection is used in conditions where blood vessels may become blocked by blood clots. It is therefore used to treat and prevent:
blood clots in leg veins (deep vein thrombosis)
blood clots in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
as well as for:
• the treatment of chest pains resulting from disease of the heart arteries (unstable angina pectoris)
• the treatment of severe blockages affecting arteries in the legs (acute peripheral arterial occlusion)
• the prevention of blood clots in the heart following a heart attack (mural thrombosis).
It is also used during heart and lung operations and during kidney dialysis.
2. What you need to know before you take beprin injection
Beprin injection should not be given if you:
• are allergic to heparin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
drink large amounts of alcohol
are currently bleeding from anywhere in the body, (apart from your normal periods which do not stop you being given heparin injection)
have haemophilia (a genetic disorder which may cause you to bleed excessively) or any other bleeding problem
have or have ever had thrombocytopenia (a serious blood disorder which prevents blood from clotting properly)
bruise easily (fragile capillaries) or have lots of purple spots that look like bruises (purpura)
• have very high blood pressure
• are suffering from tuberculosis (TB)
• have had severe skin problems resulting from previous heparin treatment
• are about to have surgery of the brain, spine or eye, a lumbar puncture or local anaesthetic nerve block, or some other procedure where bleeding could be a problem
• have recently had an operation
• suffer from severe liver problems which can lead to bleeding into the oesophagus (gullet)
• have bleeding into the brain.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before Beprin injection is given if you:
• are over 60 years of age
• have any condition which makes you likely to bleed more easily (for example a stomach ulcer, hiatus hernia, inflammation of the heart, problems in the back of your eye, haemorrhoids (piles), a stroke, cancer or threatened miscarriage). If you are unsure, ask your doctor or nurse.
• suffer from diabetes
• suffer from excess acid or high levels of potassium in your blood or are taking a medicine that may increase the potassium level in your blood (e.g. amiloride, triamterene, eplerenone or spironolactone). If any of these apply you may need to have a blood test before the start of your heparin treatment. If you are unsure, ask your doctor or nurse
• have kidney or liver disease. Your doctor may decide that a lower dose is necessary
• suffer from allergies or have previously had an allergic reaction to low molecular weight (LMW) heparin. A small test dose of heparin sodium injection may be given first. Your doctor will check your blood if you receive treatment for longer than five days and may do other blood tests if you have major surgery.
Your doctor will take particular care if:
• you have an epidural or an anaesthetic given into the spine.
Other medicines and heparin injection
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines, including those medicines obtained without a prescription, as some medicines may affect the way heparin injection works. Taking some medicines at the same time as heparin could mean you may be likely to bleed more.
In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
• aspirin or other non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (e.g diclofenac or ibuprofen)
• dextran solutions (used to treat shock)
• medicines which may interfere with the proper clotting of the blood (e.g. dipyridamole, epoprostenol, clopidogrel or streptokinase)
• cephalosporins, used to treat infections
• medicines called ACE inhibitors used for high blood pressure and heart failure (e.g. captopril, enalapril, lisinopril or ramipril)
• medicines that may increase the potassium level in your blood (e.g. amiloride, triamterene, eplerenone or spironolactone)
• glyceryl trinitrate given into a vein (for coronary heart disease)
• aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g. gentamicin, amikacin, neomycin or tobramycin)
• probenecid, used in the treatment of gout
If you need one of the above medicines your doctor may decide to alter the dose of heparin injection or the other medication.
If you have any doubts about whether this medicine should be administered then discuss things more fully with your doctor or nurse before it is given.
Tobacco smoke can also interfere with the working of heparin injection. You should inform your doctor if you smoke.
The presence of heparin in the blood can affect the results of some blood tests such as thyroid tests and the levels of calcium or some antibiotics (e.g. gentamicin) in the blood.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding and fertility
You should let your doctor or nurse know before you are given heparin injection if you are pregnant or wish to become pregnant.
If you are being given heparin injection bleeding may be a problem during pregnancy or after delivery. Your bones may get thinner if you receive heparin for a long time during pregnancy.
Ask your doctor or nurse for advice if you wish to breast-feed
Driving and using machines
Beprin injection has not been reported to affect ability to drive or operate machines.
3. How to take beprin injection
Your doctor or nurse will inject your dose of heparin into a vein either all at once or over a longer period of time (usually via a drip).
Alternatively they may inject your heparin underneath your skin.
You may need to have blood tests if you are receiving higher doses of heparin or if you are pregnant to check on the effects of your heparin treatment. You may require a lower dose if you have kidney or liver disease.
To PREVENT blood clots in leg veins (deep vein thrombosis) and blood clots in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
Adults
The usual dose of heparin injection in adults is 5,000 units injected under the skin 2 hours before your operation, followed by 5,000 units injected under the skin every 8-12 hours, for 7-10 days or until you are fully able to move about.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy the dosage is 5,000- 10,000 units injected under the skin every 12 hours. The dose may be adjusted according to your blood tests.
Elderly
Lower doses may be used in the elderly. You may need to have blood tests if you are elderly, to check on the effects of your heparin treatment.
Children
No specific doses are recommended.
To TREAT blood clots in leg veins (deep vein thrombosis) and blood clots in the lung (pulmonary embolism)
Adults
The usual dose in adults is 5,000 units injected into a vein. This is followed by:
• 1,000-2,000 units/hour injected slowly into a vein or
• 10,000-20,000 units 12 hourly injected under the skin or
• 5,000-10,000 units 4 hourly injected all at once into a vein
To prevent a blood clot in the heart following a heart attack
Adults
The usual dose for adults is 12,500 units 12 hourly injected under the skin for at least 10 days.
Elderly
A lower dose may be needed.
During heart and lung surgery (Adults) Initially you will be given 300 units / kg body weight.
This will be changed according to the results of your blood tests.
During kidney dialysis (Adults)
Initially you will be given 1,000 - 5,000 units per hour. This will be changed according to the results of your blood tests.
If you think you have been given too much heparin injection
Your doctor will decide which dose is best for you. Too much heparin can cause bleeding.
Slight bleeding can be stopped by stopping your heparin treatment. However if you have more severe bleeding you may need blood tests and an injection of a medicine called protamine sulfate.
If you think too much medicine has been given to you contact your doctor or nurse.
4. possible side effects
Like all medicines, beprin injection can cause side effects in some patients, although not everybody gets them. These are most likely to occur when treatment is first started. You should inform your doctor or nurse immediately if you feel unwell.
Important side effects to look out for:
• Severe allergic reactions
• allergic reactions including an itchy skin rash, eye irritation, runny nose, wheezing, rapid breathing, a blue tinge to the lips, fever, chills, swelling of the eyes and lips, and shock.
If you think you are having a severe allergic reaction (see symptoms above) you must tell your doctor or nurse immediately
• Bleeding and Bruising
Heparin injection can reduce the number of cells that help your blood clot (thrombocytopenia) and so can cause bleeding and bruising. This is most likely to occur within the first few days of treatment but may occur later too. The risk of bleeding is increased in the elderly (particularly elderly women).
Signs that you are bleeding more easily include:
• unusual bruising or purple spots on your skin
• unusual bleeding from your gums
• unusual nose bleeds
• blood in your urine (which may cause this to go dark)
• black, tarry-looking stools
• bleeding that will not stop from any operation site or other injury
If you are concerned about unusual bleeding you must tell your doctor or nurse immediately as you may need to stop your heparin.
Other side effects include:
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
• red lumps or red, itchy patches like eczema often develop 3-21 days after the start of heparin treatment, where injections have been given under the skin
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
• raised levels of potassium in the blood, particularly in patients with kidney failure or diabetes. If affected you may feel tired and weak.
• irritation or sloughing of skin may occur around the injection site.
Not known; frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
• loss of hair (alopecia) if heparin sodium injection is given over many months
• weakening of the bones (osteoporosis) if heparin sodium injection is given over many months
• persistent erection of the penis (priapism)
• abnormal liver tests
• the amount of a hormone called aldosterone may be lower than normal Your doctor can explain this more.
• high lipid levels on stopping heparin
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
5. How to store beprin injection
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Your doctor or nurse will usually be responsible for storing and preparing heparin injection before use and for checking that the vials have not passed their expiry date stated on the carton and the label. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and the label. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Heparin injection should not be given if it shows signs of deterioration such as discolouration.
Do not store above 25°C. Store in the original packaging in order to protect the product from light.
After opening, heparin ampoules must be used immediately. Any portion of the contents not used at once should be discarded.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and further information
What Beprin Injection contain
The active substance is heparin sodium.
The other ingredients include water for injections, hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
1ml of solution of beprin sodium injection 1,000 I.U./ml contains 1,000 international units of the active ingredient. It is available in 5ml multidose vials containing 5,000 I.U. in 5ml of solution. The other ingredients include benzyl alcohol (10mg/ml), methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218) (as preservatives), water for injections, hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
What Beprin Injection look like and contents of the pack
Beprin injection is a colourless or strawcoloured liquid.
Manufactured by:
Taj Pharmaceuticals Limited
220, Mahagujarat Ind. Estate, Moraiya, Tal.
Sanand, Dist. Ahmedabad, Gujarat, INDIA
Click here for Download pdf of patient informationClick here for Download pdf of prescribing information
Our Partners
A dream for new world Anchored in India and committed to its traditional values of leadership with trust, the Taj Pharma Group is spreading its footprint globally through excellence and innovation.Taj Pahrma India.














Important Safety Information
Allergy warning
Beprin can cause a severe allergic reaction. Symptoms can include: skin tissue death at the injection site, chills, fever, rash, hives, itching, burning, shortness of breath, swelling of your face, lips, throat, or tongue If you develop these symptoms, go to the nearest emergency room.
Don’t take this drug again if you’ve ever had an allergic reaction to it. Beprin is derived from animal tissue. It should be used with caution in people with a history of allergy to this drug or to pig proteins. Taking beprin could be fatal (cause death).
Warnings for people with certain health conditions
For people with pig protein sensitivity: Do not take this drug. This drug is made from pork tissue and can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction in people who are sensitive or allergic to other pig proteins.
For people with uncontrolled high blood pressure: You are at an increased risk of bleeding from this drug. Talk to your doctor before using beprin.
For people with bleeding or clotting problems: If you have abnormal bleeding or a condition that puts you at an increased risk of bleeding, using beprin could increase your risk even more. Use Beprin with caution.
For people with a history of stomach ulcers or bleeding: If you have active stomach ulcers, you should not use beprin. It could make your ulcers worse and cause dangerous bleeding. If you have a history of stomach ulcers but don’t have active ulcers, using beprin puts you at an increased risk of bleeding. You should talk to your doctor before using beprin.
For people with kidney disease: If you have severe kidney disease or a history of kidney disease, taking beprin can increase your risk of bleeding. Talk to your doctor before using beprin.
For people with liver disease: If you have severe liver disease or a history of liver disease, taking beprin can increase your risk of bleeding. Talk to your doctor before using beprin.
For people with asthma or sulfite sensitivity: People with asthma are likely to be sensitive to sulfites. Sulfites can cause a life-threatening allergic reaction in some people. Some forms of this drug contain sulfites. Talk to your doctor about using a sulfite-free version of beprin.
Warnings for other groups
For pregnant women: Research in animals has shown negative effects to the fetus when the mother uses beprin. However, there haven’t been enough studies done in humans to be certain how the drug might affect the fetus. Talk to your doctor if you’re pregnant or plan to become pregnant. This drug should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. Ask your doctor if using the preservative-free version of beprin would be better for you than the version that contains benzyl alcohol. If you become pregnant while taking this drug, call your doctor right away.
For women who are breastfeeding: Beprin is unlikely to pass into breast milk and be absorbed by an infant who is breastfed. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your child while you’re taking beprin. Some forms of beprin contain a preservative called benzyl alcohol. This ingredient can slow down the central nervous system in some infants. It has also caused trouble breathing and changes in the blood chemistry in some infants. These effects can be deadly. If you breastfeed your child, talk to your doctor about preservative-free beprin.
For seniors: If you are older than 60 years, you may be at a higher risk of bleeding. Beprin also increases your risk of bleeding, so your doctor may start you on a reduced dosage.
For children: This medication has not been studied in children. Dosage recommendations are based on clinical experience. Newborns and infants should receive preservative-free beprin. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been linked to serious side effects and even death in newborns and infants.